VIM is a command-line text editor available in most of Linux distributions. It’s very useful when no GUI (Graphical User Interface) is available, to edit and save files.
Installation
To install VIM, for example on Debian:
sudo apt-get install -y vimOpen a file with VIM
To open a file, from a shell:
vim /path/to/file.ext
Edit a file
When the file is open, it’s impossible to directly write into it:
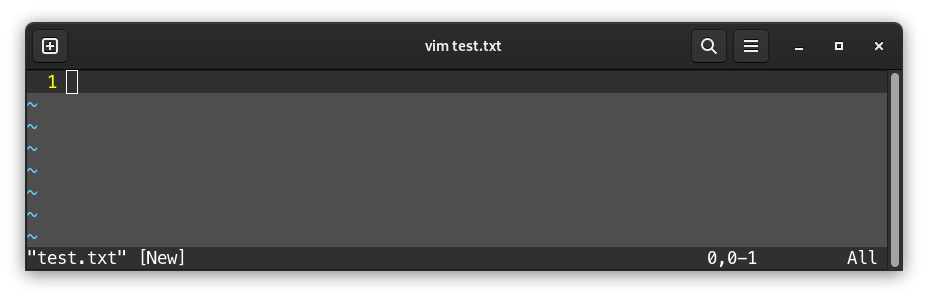
To be able to write into it, press the i key to switch to insertion mode (-- INSERT -- should appear at the bottom of the screen):
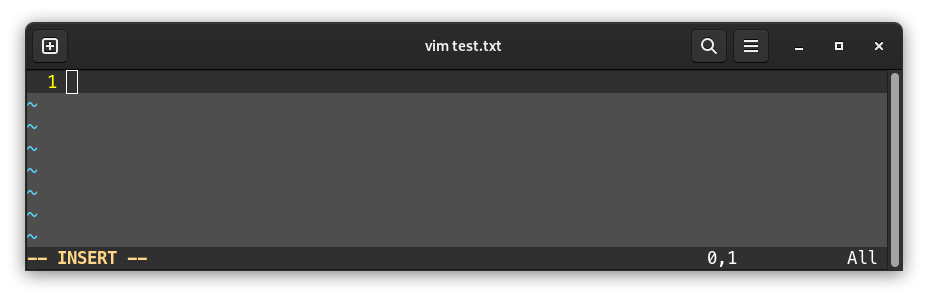
It’s then possible to edit the file:
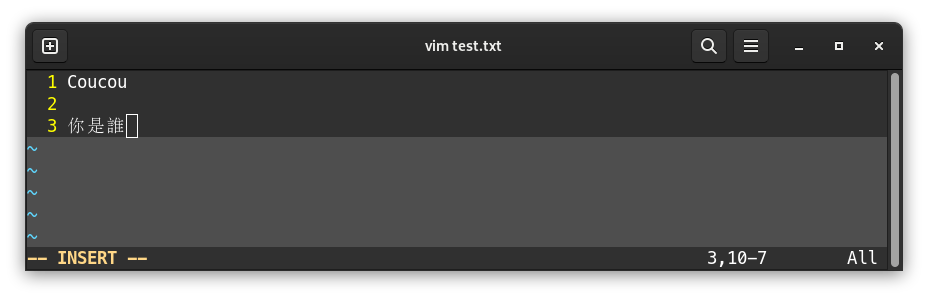
Once you’re finished with writing contents, press the Echap key to quit insertion mode. -- INSERT -- disappears from the bottom screen, and it’s not possible to write into the file:
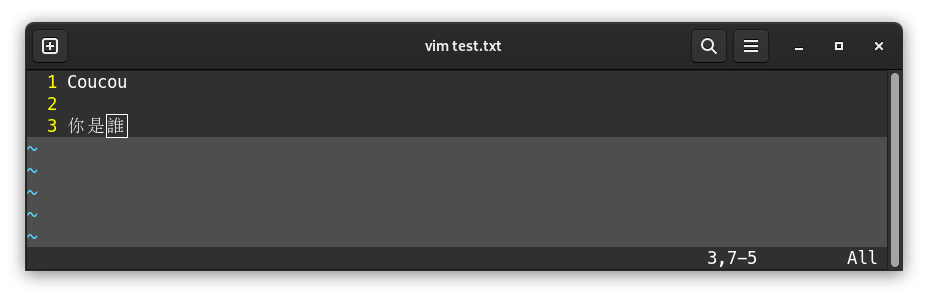
Once Echap is pressed, one may want to quit, save (or both at the same time), or quit without saving (after a mistake), etc…
To perform these actions, there are various commands.
Run a command
After leaving insertion mode with Echap, it’s possible to run a command on the file: save, save & quit, go to line, copy, paste…
To run a command, first press : key, and then type the command.
Save and quit
To save and quit: :wq
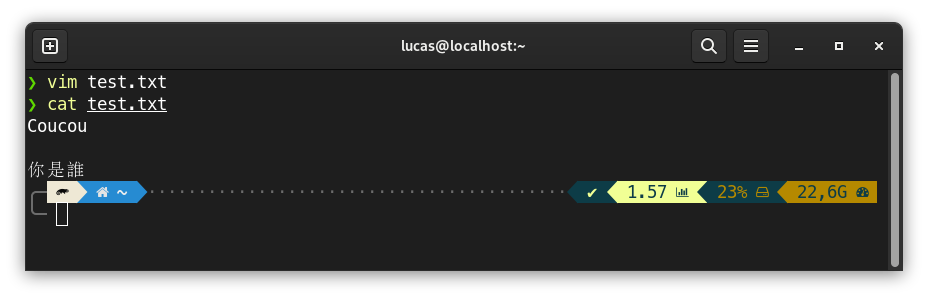
We can then check if the file was correctly saved:
Save without quitting
To save only (without quitting): :w
If we add text into a file, and then press Echap and :w:
Then Enter:
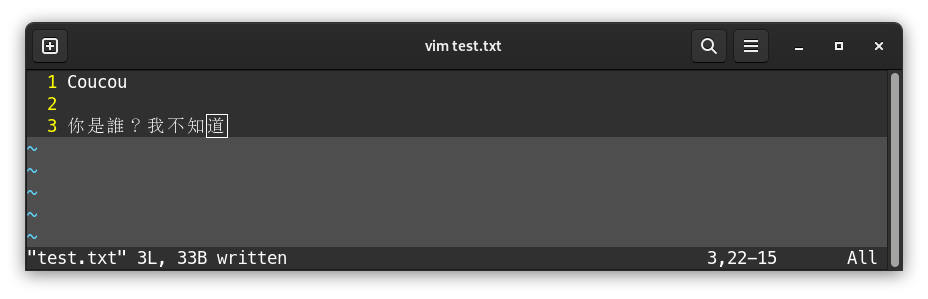
It is then possible to switch back to insertion mode to continue editing the file.
Quit without saving
To quit VIM without saving the file: :q!
Go to line
To go to a line XXX, first press : then the line number: :XXX
Display line numbers
On the left side, if there are no line numbers, display it with :set nu
Enable syntax highlighting
Syntax highlighting should be automatic. VIM has built-in suppot for hundreds of programming languages and file formats.
However, if the file doesn’t have syntax highlighting, it’s possible to enable it with :syn on.
It is then possible to apply a color theme with, for instance, :colo desert.
Cut/Copy/Paste
In command mode, it’s possible to cut/copy/paste lines.
For these features, there is no need to press : prior to the command.
Pressing d 2 times (so dd) cuts the current line.
Pressing y 2 times (so yy) copies the current line.
Then, to paste cut or copied contents, press p.
Find text
To find text, we won’t use : but rather /, followed by the text. Then we run the search with Enter:
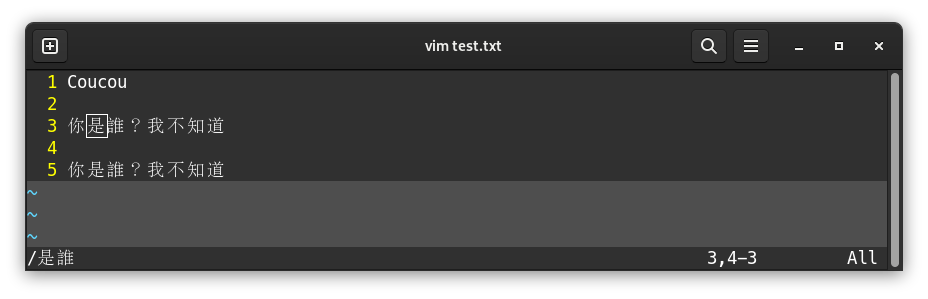
VIM places the cursor on the first found occurence. If there are multiple results, such as below, it’s possible to go to the next result by pressing n. If the search reaches end of file, VIM goes back to the first occurence, and notifies it at the bottom of the screen:
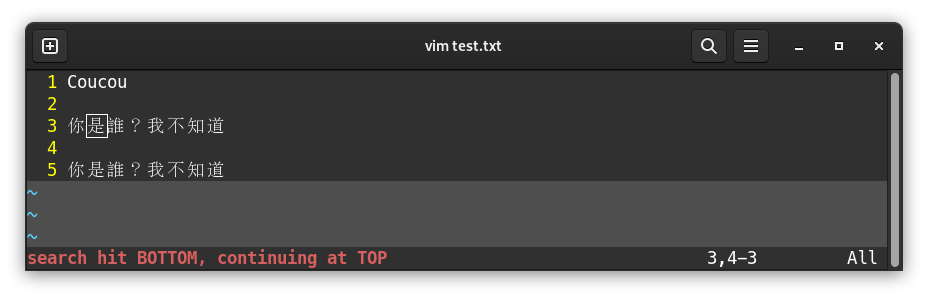
To go to previous occurence, press N instead of n.